Water-based coating additive - substrate wetting agent
Categories: Homepage Recommended News
Categories: Technical exchange
Time:2024-04-25 10:12
In practical applications, water-based coatings, due to their high surface tension and the complex diversity of industrial construction substrates, often exhibit insufficient wetting of the coating film and substrate. This leads to surface defects such as pinholes, bubbles, and depressions, affecting the quality and appearance of the coating.
Substrate wetting agents and their mechanism of action
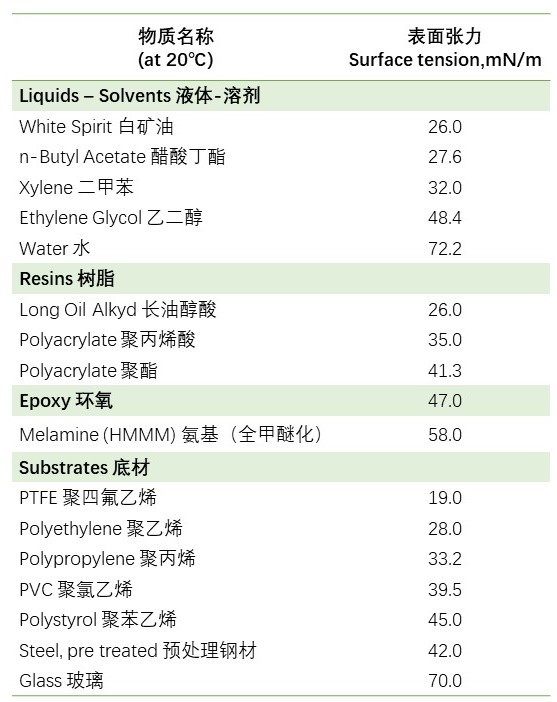
Substrate wetting agents belong to surfactants. They are substances that can reduce the surface tension between the coating and the substrate. By improving the contact state between the coating and the substrate, they enable the coating to better wet the substrate surface. The main mechanism of action of substrate wetting agents is to reduce the surface tension between the coating and the substrate. The wetting of a liquid on a solid surface is related to the contact angle, which in turn is related to the surface tension. Sufficient wetting only occurs when the surface tension of the liquid is less than that of the substrate. The higher the surface tension, the more likely surface defects are to occur.
Table 1-Surface tension of common substances
The role of substrate wetting agents in coating formulations
Adding substrate wetting agents to coating formulations has several important roles. First, when encountering substrates with low surface tension, wetting agents or formulation adjustments are needed to lower the surface tension of the coating system below that of the substrate, thus achieving good substrate wetting. Second, substrate wetting improves the wetting and spreading of the coating on the substrate, increasing the smoothness of the coating surface. In addition, it can prevent defects such as shrinkage and edge shrinkage caused by low substrate surface tension.
Types of substrate wetting agents
Wetting agents come in various types. According to the object being wetted, they are classified into substrate wetting agents, wetting leveling agents, and wetting dispersing agents. The former two focus on wetting the substrate and the coated surface, while the latter promotes the dispersion of pigments and fillers in the coating base material. Common substrate wetting agents include ethoxylated adducts (e.g., polyoxyethylene nonylphenol), polyether silicone, non-ionic fluorocarbon polymers, and diyne diol compounds.
Characteristics of substrate wetting agents
1. Low surface tension, good wetting performance;
2. Low foaming or defoaming effect;
3. No adverse effects on other properties of the coating;
4. Good hydrolysis resistance;
5. Good versatility in coating formulations;
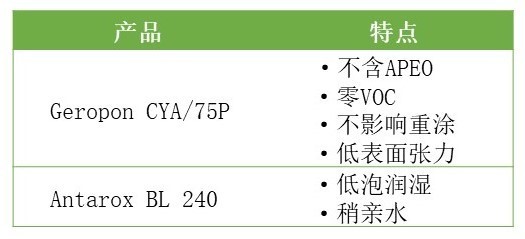
Haochang substrate wetting agent products