Overview of Surfactants (Part 2): Functions of Surfactants and HLB Value
Categories: Homepage Recommended News
Categories: Technical exchange
Time:2022-11-28 15:59
Types of Surfactants
It is generally considered appropriate to classify them according to their chemical structure. That is, after the surfactant is dissolved in water, depending on whether ions are generated and their electrical properties, it is divided into ionic surfactants and non-ionic surfactants. According to the dissociation properties of the polar groups, it can be divided into the following four categories:
Anionic surfactants: such as sodium stearate, sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate
Cationic surfactants: such as hexadecyldimethylchlorine ammonium
Amphoteric surfactants: such as lecithin, amino acid type, betaine type
Non-ionic surfactants: such as alkyl glucoside (APG), fatty acid glycerides, sorbitan fatty acid esters (Span), polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid esters (Tween), polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, etc.
HLB Value
HLB value (Hydrophile-Lipophile Balance Number), also known as the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance value, or water-oil degree. In 1949, W.C. Griffin first proposed the HLB value theory, which explains the balance between the hydrophilic group and the lipophilic group in surfactant molecules. In HLB, H "Hydrophile" represents hydrophilicity, L is "Lipophilic" represents lipophilicity, and B is "Balance" which means balance.
HLB = Hydrophilicity of hydrophilic group / Lipophilicity of lipophilic group
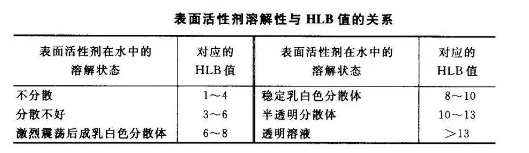
The lipophilic or hydrophilic degree of a surfactant can be judged by the size of the HLB value. The larger the HLB value, the stronger the hydrophilicity; the smaller the HLB value, the stronger the lipophilicity. Generally, the HLB value ranges from 1 to 40. The HLB value of paraffin, which is composed entirely of saturated alkane groups and has the highest hydrophobicity, is defined as 0, and the HLB value of sodium lauryl sulfate, which has the highest hydrophilicity, is defined as 40. HLB is related to the hydrophilic and lipophilic properties of the surfactant, as well as to the basic properties of the surfactant such as surface (interface) tension, adsorption on the interface, emulsification and emulsion stability, dispersibility, solubility, detergency, etc., and is also related to the application performance of the surfactant. HLB has important reference value in practical application.
Surfactants with different HLB values have different uses.
The HLB value of non-ionic surfactants can also be calculated using some empirical formulas, such as:
HLB = 7 + 11.7 lg M w /M 0
In the formula, M w and M 0 are the molecular weights of the hydrophilic group and the lipophilic group in the surfactant molecule, respectively.
The HLB value of a mixed emulsifier can be calculated using the following formula:
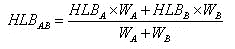
In the formula, W A and W B represent the amounts of surfactants A and B respectively, HLBA and HLBB are the HLB values of A and B respectively, and HLB AB is the HLB value of the mixed surfactant.
HLB Value and Application
Based on some empirical data of HLB values, it can be used as a reference for application.
HLB value 1~3 is used as an antifoaming agent;
HLB value 3~6 is used as a W/O emulsifier;
HLB value 7~9 is used as a wetting agent;
HLB value 8~18 is used as an O/W emulsifier;
HLB value 13~15 is used as a detergent;
HLB value 15~18 is used as a solubilizer.