Overview of Surfactants (Part 1) Development History
Categories: Homepage Recommended News
Categories: Technical exchange
Time:2022-10-25 10:06
What are surfactants?
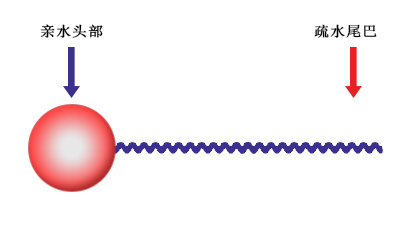
Surfactants are substances that, when added in small amounts, can significantly change the interfacial state of their solution system. This sounds difficult to understand, but surfactants can be described as a matchstick, with a slender lipophilic end on one side and a round hydrophilic end on the other. The lipophilic end readily combines with oily substances, while the hydrophilic end readily combines with water. The lipophilic end acts like a claw, grabbing oil stains and bringing them into the water; this is the most common application of detergents. Detergents are one application of surfactants.
History of Surfactants
Before the rise of modern chemical industry, our ancestors already used some natural substances with washing functions, such as soap pods and Sapindus mukorossi. Literature shows that soap pods were used to wash clothes and hair during the Qin and Han dynasties, becoming widespread during the Sui and Tang dynasties. By the Song dynasty, with its highly developed science and culture, soap pods underwent further innovation and development. They were crushed and ground into a fine powder, and then supplemented with spices to create truly natural soap, which became a commodity. Its main component, saponin, is a natural surfactant.
As early as 2500 BC, there were records in the West of using oils and plant ash containing potassium carbonate to produce potassium soap, and using this soap to wash wool. The main chemical component of this soap is potassium oleate, which modern chemistry calls an anionic surfactant.
In the early 19th century, with the development of the petroleum industry, people reacted wax with sulfuric acid and then neutralized it with caustic soda to produce petroleum sulfonate soap, called green sodium (the first detergent made from mineral raw materials). During World War I, the large output of coal promoted the development of the coal chemical industry, leading to the development of short-chain alkyl and naphthalene sulfonate surfactants, such as propyl naphthalene sulfonate and butyl naphthalene sulfonate.
From 1920-1930, fatty alcohol sulfation produced alkyl sulfates. In the 1930s, long-chain alkyl and phenyl groups appeared in the United States. After World War I, Germany developed glycol derivatives, such as polyethylene glycol derivatives. Polyethylene glycol combined with various organic compounds (including alcohols, acids, esters, amines, amides, etc.) to form a variety of non-ionic surfactants with excellent properties.
After the 1950s, with the advancement of chemical technology, the number of surfactant varieties in China has continued to increase, currently exceeding 4000.
With economic development and improvement in the standard of living, surfactants will continue to keep pace with the times, developing towards green, environmentally friendly, and functional directions. The goal is to ensure the green and ecological safety of products while focusing on functionality, to reduce the impact on the environment and harm to humans.


